NGS Custom Panel Design
Focus your sequencing efforts on the targets important to you
Digital NGS with QIAseq Targeted Panels
Our QIAseq Targeted Panels incorporate molecular barcode technology to provide accurate digital DNA and RNA sequencing. This unique approach overcomes the issues of PCR duplicates, false positives and library bias, enabling detection of low-frequency variants and accurate quantitative gene expression profiling. Choose from our expertly curated cataloged panels, or design a custom panel for your particular targets of interest.

Confidently distinguish unique molecules, revealing meaningful insights for results that make an impact.
Terms to know
Target enrichment: process to enhance NGS experiments by sequencing specific regions of interest, instead of the entire genome, effectively increasing the sequencing depth and sample throughput while minimizing cost.
Single primer extension: an amplicon enrichment strategy in which each the genomic target is amplified by one target-specific primer and one universal primer; enables a flexible design approach and more efficient primer utilization when compared to conventional two-primer methods. Read this article to find out more.
Unique molecular index (UMI): a 12-base random unique nucleotide sequence that is attached to an adapter and ligated to the original DNA or cDNA sample prior to amplification; enables both bioinformatic correction of PCR amplification errors and deduplication of reads for accurate quantification and variant calling. Also known as molecular barcode.
Digital sequencing: sequencing strategy in which UMIs are incorporated into the starting DNA or cDNA before any amplification takes place, to preserve the uniqueness of the starting molecules and overcome the issues of PCR duplicates, false positives and library bias.
QIAseq Targeted DNA Panels: platform-agnostic solution for constructing NGS libraries from enriched targets. Incorporate UMIs and a single primer extension design strategy. All required primers are combined into an individual pool for enrichment and library construction. Platform-specific indexes are available separately and allow sample multiplexing in the sequencing run.
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP): a single-base difference found when comparing the same DNA sequence from two different individuals.
Browser extensible data (BED): the human-readable file format showing the defined chromosomal coordinates as a genomic region of interest (ROI).
Discover QIAseq Targeted DNA Panels
Use the custom builder tool to design and order the exact targeted DNA sequencing panel for your research.
Designing a custom DNA panel
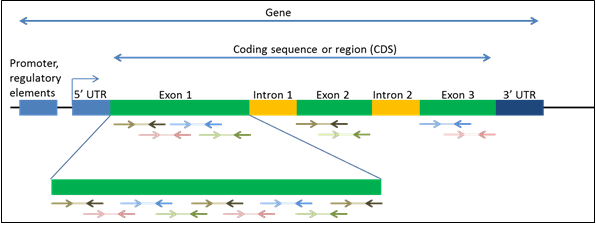
The QIAseq Targeted DNA Custom Panel Builder enables you to design and order the targeted DNA sequencing assay of your choosing. You can target complete genes, specific exons, hotspots or any defined genomic region of interest in the human genome.
The following types of custom DNA panels can be created:
- Custom panels – enter your own content, such as genes or genomic coordinates, into the QIAseq Targeted DNA Custom Builder to design a custom panel
- Extended panels – add up to 100 primers to any cataloged panel to extend its content; visit the QIAseq Targeted DNA Extended Panels catalog page, and select “Extend” next to the relevant catalog panel to get started.
- Booster panels – configure a spike-in pool of up to 100 primers to either boost coverage of specific areas or augment targets across specific genomic regions of any panel (cataloged, extended, or custom). Delivered as a single pool that can be spiked into the existing panel; visit the QIAseq Targeted DNA Booster Panels catalog page, and select “Boost” next to the relevant catalog panel to get started
When possible, the builder spaces primer binding sites by a maximum of 150 bp, to enable efficient enrichment of FFPE and cfDNA samples. In general, the following guidelines apply.
Targeting genes or exons
Use the Gene tab in the custom builder to enter NCBI Gene Symbols (e.g., CASP2) or Entrez GeneIDs (e.g., 835). When you specify gene symbols, the builder adds 5 bp of flanking intronic region around each coding exon to the target region. For specific exons, enter NCBI Transcript Refseq IDs (e.g., NM_032983, NP_116765).
Targeting SNPs, hotspots or intronic regions by specifying genomic coordinates
Use the Genomic Coordinates tab in the custom builder to enter the chromosome number and genomic start/stop coordinates of your areas of interest using the BED format described below:
- Example: chr1 100326942 100327378
- Use one line for each chromosome and location
- Comma, semicolon or tab stop can be used as separator
- Enter lowercase text for chromosome without any spaces between “chr” and “1”, “11”, “X”, etc.