GeneGlobe ID: SMH-046AA | Cat. No.: 337021 | qBiomarker Somatic Mutation PCR Arrays
qBiomarker™ Somatic Mutation PCR Array Human Myelodysplastic Syndromes
Product Specification
PCR plate and master mix
Target List
ASXL1
Most frequently observed mutations in this gene are C-terminal truncations that lose the interaction domain with RARA, the poly-serine region, or the atypical PHD-type domain. Other truncations also lose part of the NCOA1 interaction domain and a glycine-rich region.
CBL
The most frequently occurring mutations in this gene reside in its RING-type, or zinc finger-like, domain in an Asp/Glu-rich (acidic) region likely involved in its ubiquitination activity. Other mutations include p.R420Q and p.K382E, which impair CBL-mediated degradation of cell-surface receptors in a dominant-negative fashion, and p.Y371H, which should reduce tyrosine phosphorylation by the insulin receptor.
DNMT3A
Mutations are frequently observed in the domain conserved among S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferases superfamily members.
EZH2
All detected mutations lie in the SET domain responsible for histone lysine methyltransferase activity.
IDH1
Most of these mutations abolish magnesium binding and alter the enzyme's activity to convert alpha-ketoglutarate into R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate instead of isocitrate into alpha-ketoglutarate.
IDH2
These mutations all lie in the substrate binding domain, and one (p.R140Q) is associated with D-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria.
NRAS
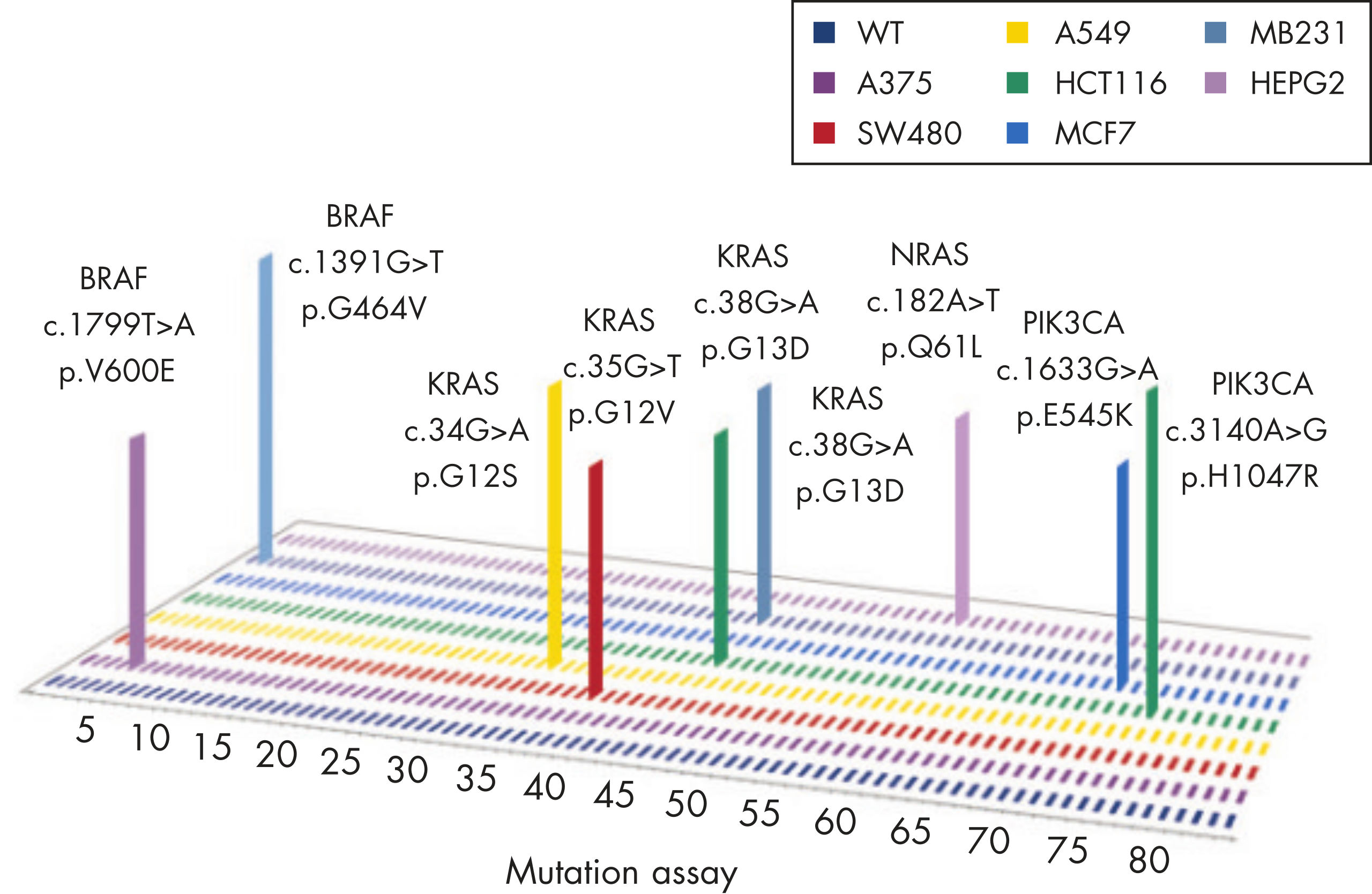
The mutation assays detect the most important NRAS variants, all found in codons 12, 13, and 61.
RUNX1
RUNX1 is the alpha subunit of the core binding factor that is thought to be involved in normal hematopoiesis. Chromosomal translocations involving this gene have been associated with several types of leukemia.
SF3B1
The most frequently occurring mutations in this gene reside in any one of its 11 HEAT repeats. These domains are possibly protein-protein interaction surfaces or involved in intracellular transport processes.
SRSF2
Mutations frequently occur at a proline residue in amino acid position 95.
TET2
The most common variants of this gene are C-terminal truncations missing its two glutamine-rich regions, all of its metal binding site residues, and a phosphoserine and a phosphotyrosine site.
TP53
The most frequently detected somatic TP53 mutations occur in the DNA-binding domain which disrupt DNA binding and/or protein structure.
U2AF1
Mutations frequently occur at two residues each in different zinc fingers (C3H1-type domains) likely involved in RNA binding.
Product Resources
File Size: 138.97 KBLanguage: English
Resources
Supplementary Protocols (7)
Download Files (1)
Safety Data Sheets (1)
Instrument Technical Documents (2)
Performance Data (3)
Kit Handbooks (1)
White Papers (1)
Articles (1)
Application Notes (1)
Certificates of Analysis (1)
Introducing the qBiomarker™ Somatic Mutation PCR Array Human Myelodysplastic Syndromes, a cutting-edge addition to our qBiomarker Somatic Mutation PCR Arrays lineup, specifically designed for Mutation/Variant Detection applications. This premium product offers unparalleled performance for researchers working with Human models. Leveraging advanced technology, the qBiomarker™ Somatic Mutation PCR Array Human Myelodysplastic Syndromes facilitates accurate and reliable results, making it an indispensable tool for your scientific investigations. Whether you're conducting Mutation/Variant Detection, or any other sophisticated analyses, this product from our qBiomarker Somatic Mutation PCR Arrays collection ensures optimal efficiency and reproducibility for Human studies. Embrace the future of research with qBiomarker™ Somatic Mutation PCR Array Human Myelodysplastic Syndromes and elevate your work to new heights.