GeneGlobe ID: SMH-022AA | Cat. No.: 337021 | qBiomarker Somatic Mutation PCR Arrays
qBiomarker™ Somatic Mutation PCR Array Human Hematopoietic Neoplasms
Product Specification
PCR plate and master mix
Target List
ABL1
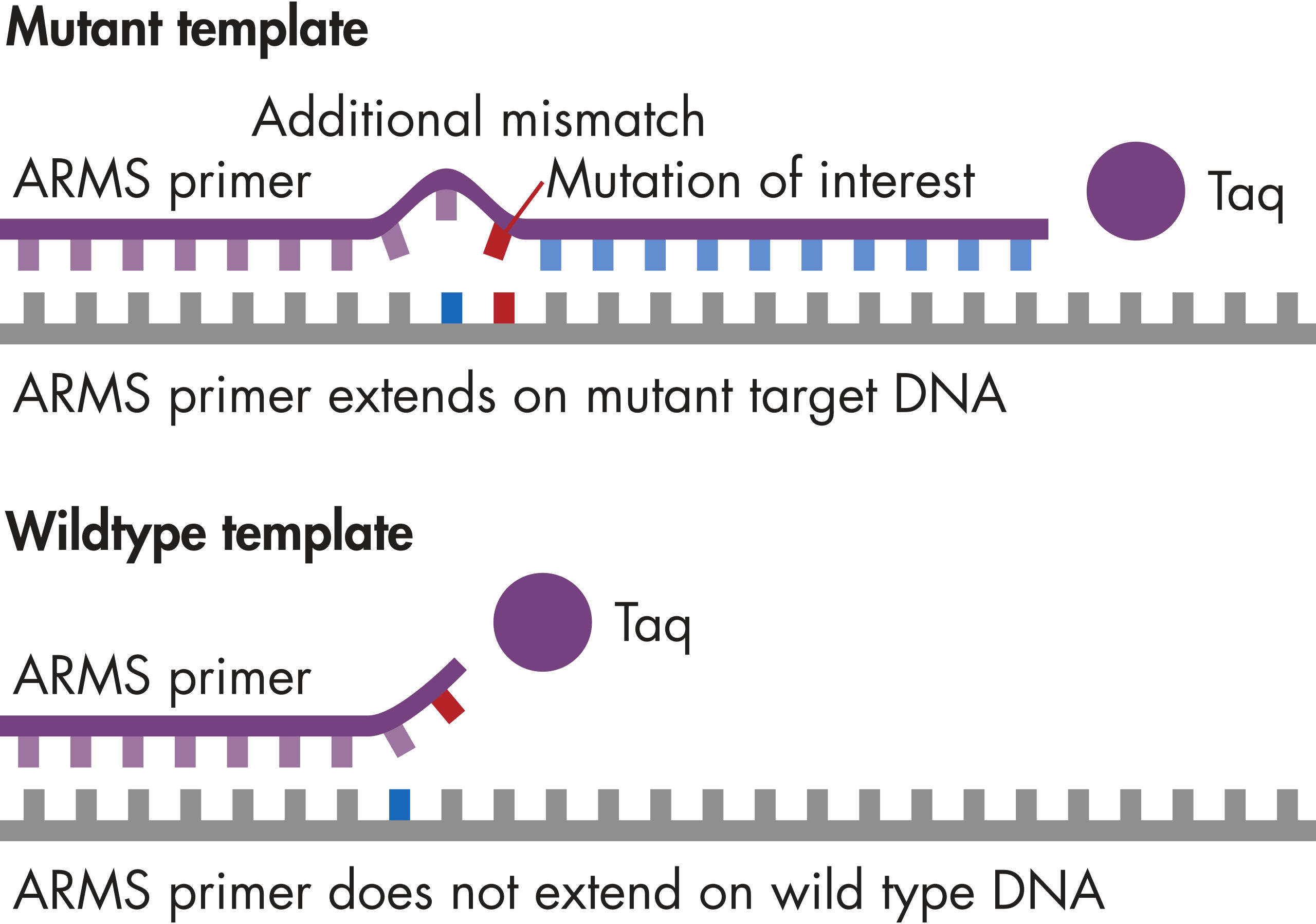
The mutations queried by these assays mostly lie in the protein kinase domain.
CEBPA
The p.K304_Q305insL mutation lies in the DNA binding basic motif of the protein.
CSF1R
This mutation near the C-terminus that corresponds to SNP variant rs1801271 abolishes the down-regulation of activated CSF1R.
FLT3
The most frequently identified FLT3 variants include point mutations, insertions and deletions in the juxtamembrane and activation loop domains of the protein.
GATA1
GATA1 plays an important role in erythroid development by regulating the switch of fetal hemoglobin to adult hemoglobin. Mutations in this gene have been associated with X-linked dyserythropoietic anemia and thrombocytopenia.
GATA2
GATA2 is a negative regulator of hematopoietic stem cell and progenitor cell differentiation. This mutation lies within the second zinc finger domain and causes a gain-of-function that increases transactivation activity and enhances inhibition of PU.1 activity, a major regulator of myelopoiesis.
IDH1
Most of these mutations abolish magnesium binding and alter the enzyme's activity to convert alpha-ketoglutarate into R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate instead of isocitrate into alpha-ketoglutarate.
IDH2
These mutations all lie in the substrate binding domain, and one (p.R140Q) is associated with D-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria.
JAK2
Most of these mutations lie in protein kinase domain 1. One mutation (p.V615F) confers cytokine-independent growth to BaF3 pro-B cells. Mutations at R683 lead to constitutive tyrosine phosphorylation activity promoting cytokine hypersensitivity and are associated with susceptibility to Budd-Chiari syndrome.
KIT
The most frequently identified KIT gain-of-function mutations include the D816V point mutation; point mutations in, and a deletion of, exon 11 (the juxtamembrane domain); an exon 9 insertion; as well as exon 13 point mutations.
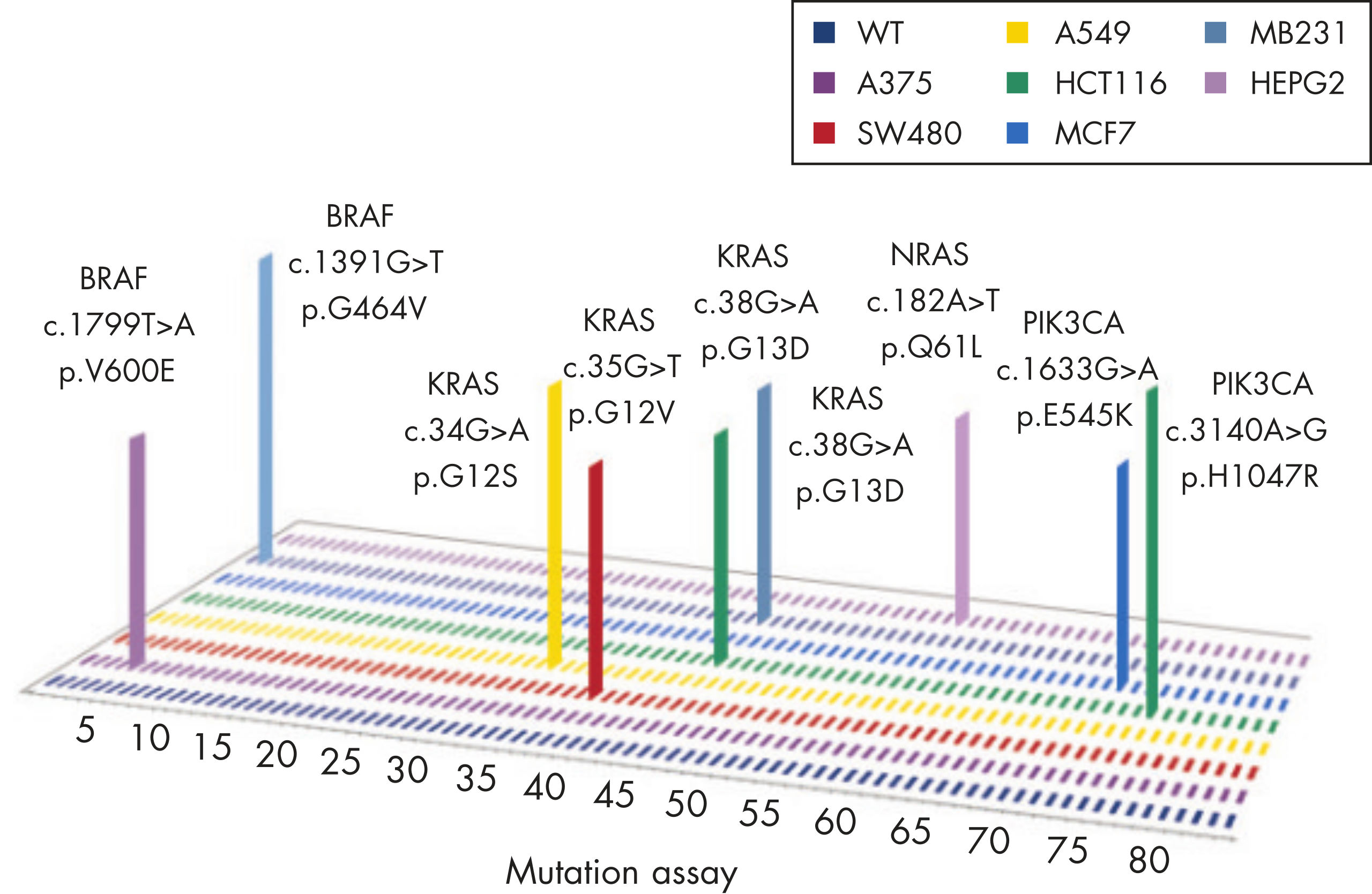
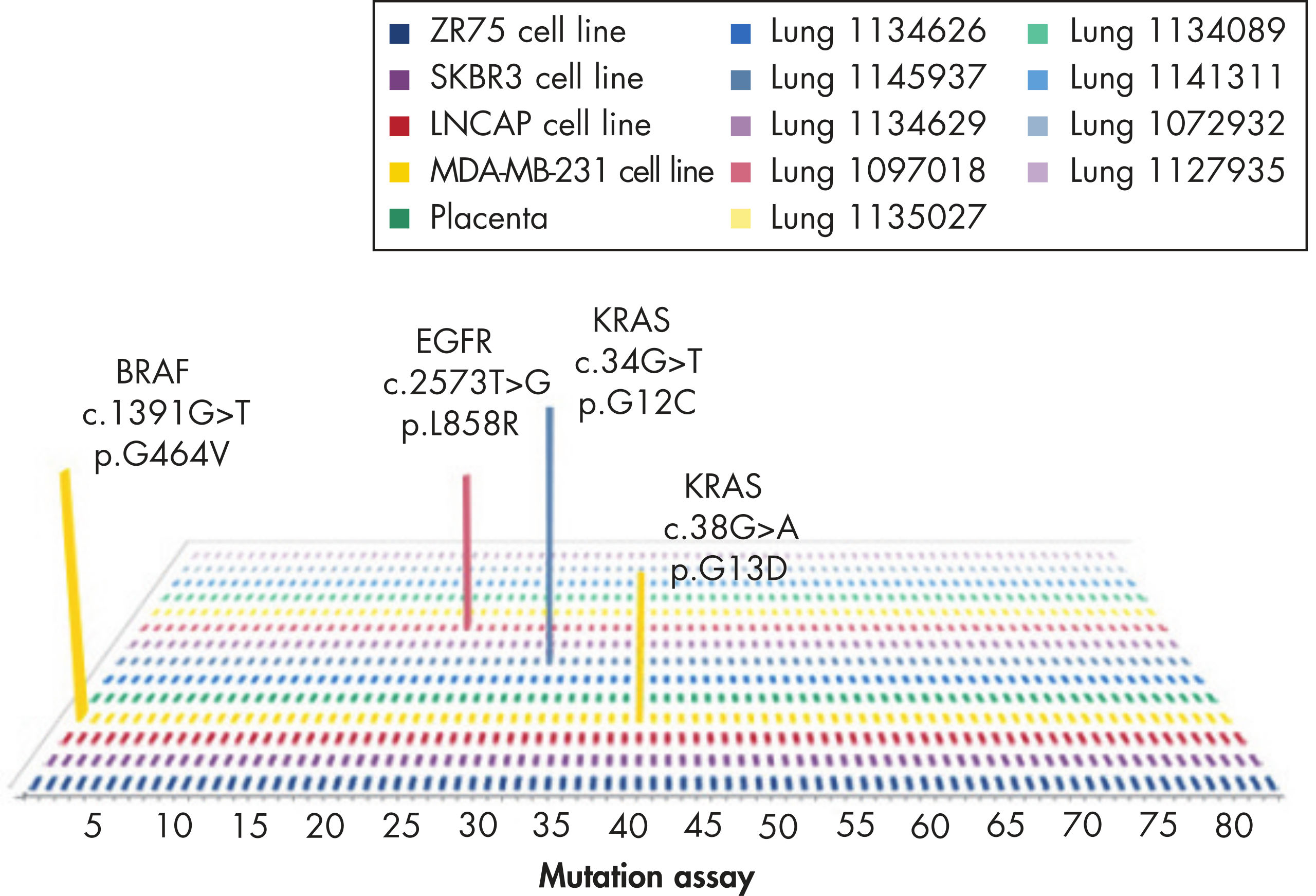
KRAS
The mutation assays detect the most frequently occurring KRAS mutations in codons 12, 13, and 61. Mutations at these positions reduce the protein’s intrinsic GTPase activity and/or cause it to become unresponsive to RasGAP.
MPL
These mutations are predicted to lie at a junction between a transmembrane helix and a cytoplasmic domain.
NPM1
NPM1 encodes a phosphoprotein that shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm and is thought to be involved in regulation of the ARF/p53 pathway. A number of gene fusion events with NPM1 have been characterized, in particular the anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene on chromosome 2. Mutations in this gene are associated with acute myeloid leukemia.
NRAS
The mutation assays detect the most important NRAS variants, all found in codons 12, 13, and 61.
PTPN11
The most frequently identified PTPN11 variants include mutations in or near the N-terminal SH2 domain and PTP-interacting surface as well as mutations that affect substrate specificity.
RUNX1
RUNX1 is the alpha subunit of the core binding factor that is thought to be involved in normal hematopoiesis. Chromosomal translocations involving this gene have been associated with several types of leukemia.
TP53
The most frequently detected somatic TP53 mutations occur in the DNA-binding domain which disrupt DNA binding and/or protein structure.
WT1
The WT1 transcription factor plays an essential role in normal urogenital system development. A small subset of patients with Wilm's tumors contains mutations in this gene.
Product Resources
File Size: 139.65 KBLanguage: English
Resources
Supplementary Protocols (7)
Download Files (1)
Safety Data Sheets (1)
Instrument Technical Documents (2)
Performance Data (3)
Kit Handbooks (1)
White Papers (1)
Articles (1)
Application Notes (1)
Certificates of Analysis (1)
Introducing the qBiomarker™ Somatic Mutation PCR Array Human Hematopoietic Neoplasms, a cutting-edge addition to our qBiomarker Somatic Mutation PCR Arrays lineup, specifically designed for Mutation/Variant Detection applications. This premium product offers unparalleled performance for researchers working with Human models. Leveraging advanced technology, the qBiomarker™ Somatic Mutation PCR Array Human Hematopoietic Neoplasms facilitates accurate and reliable results, making it an indispensable tool for your scientific investigations. Whether you're conducting Mutation/Variant Detection, or any other sophisticated analyses, this product from our qBiomarker Somatic Mutation PCR Arrays collection ensures optimal efficiency and reproducibility for Human studies. Embrace the future of research with qBiomarker™ Somatic Mutation PCR Array Human Hematopoietic Neoplasms and elevate your work to new heights.