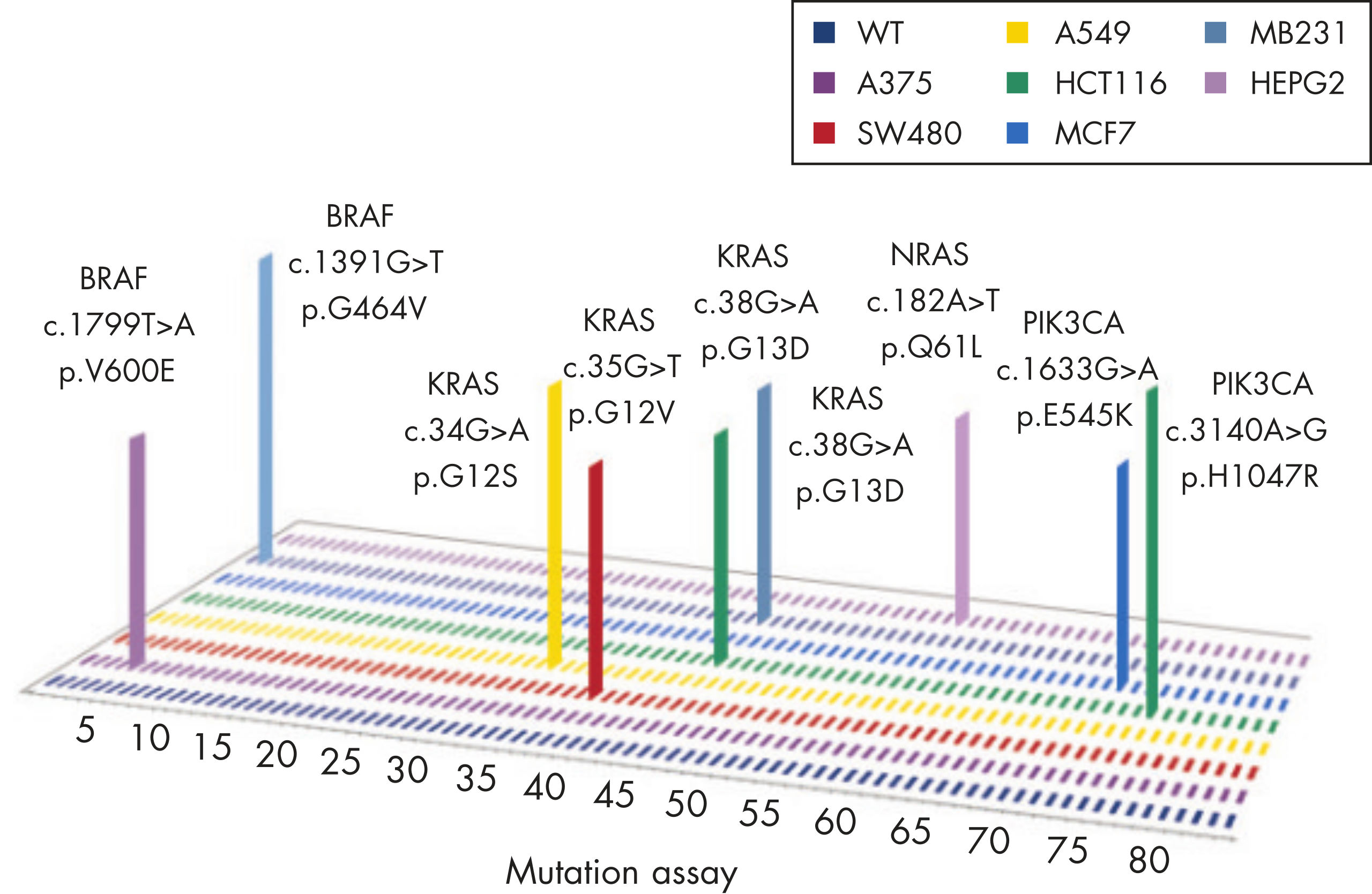
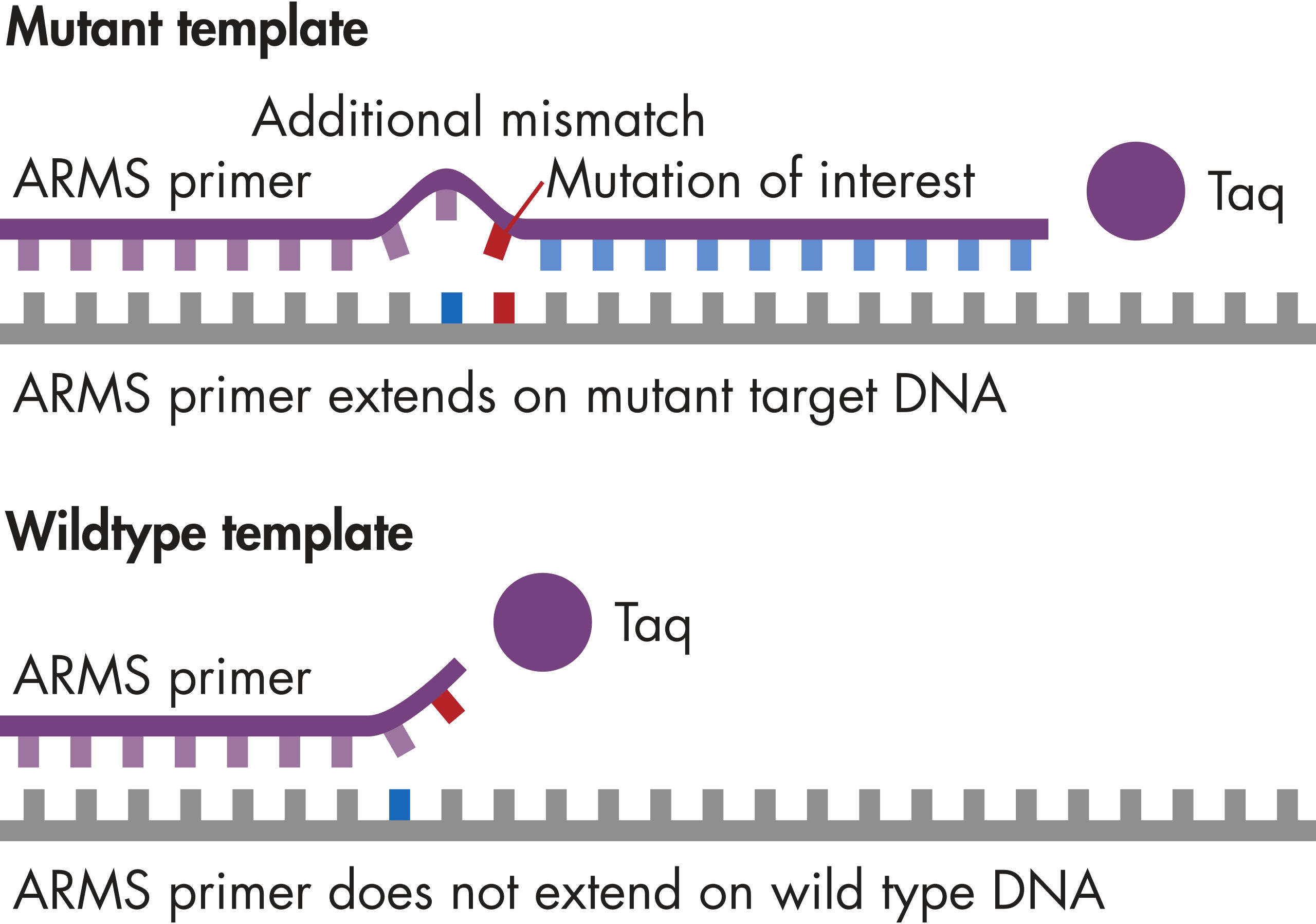
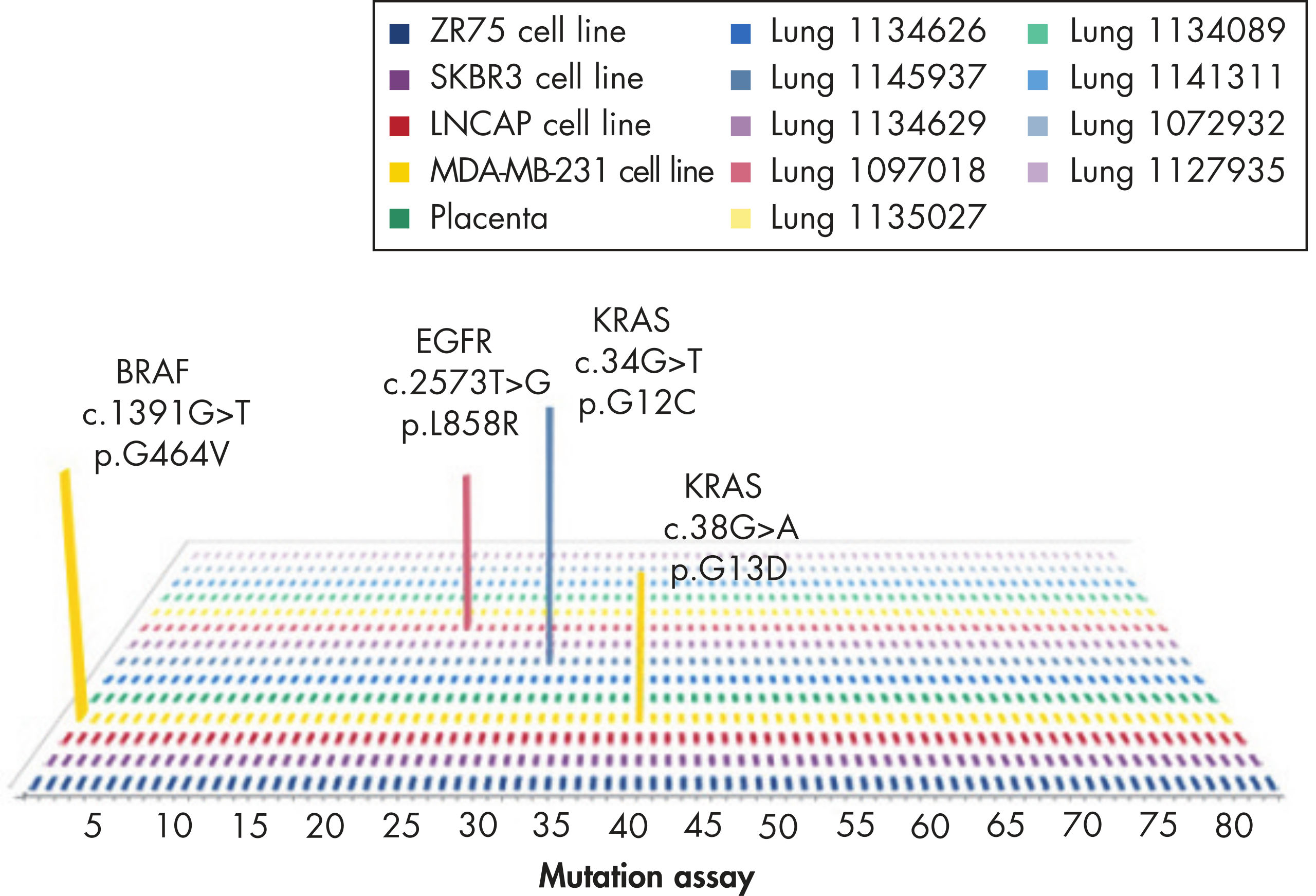
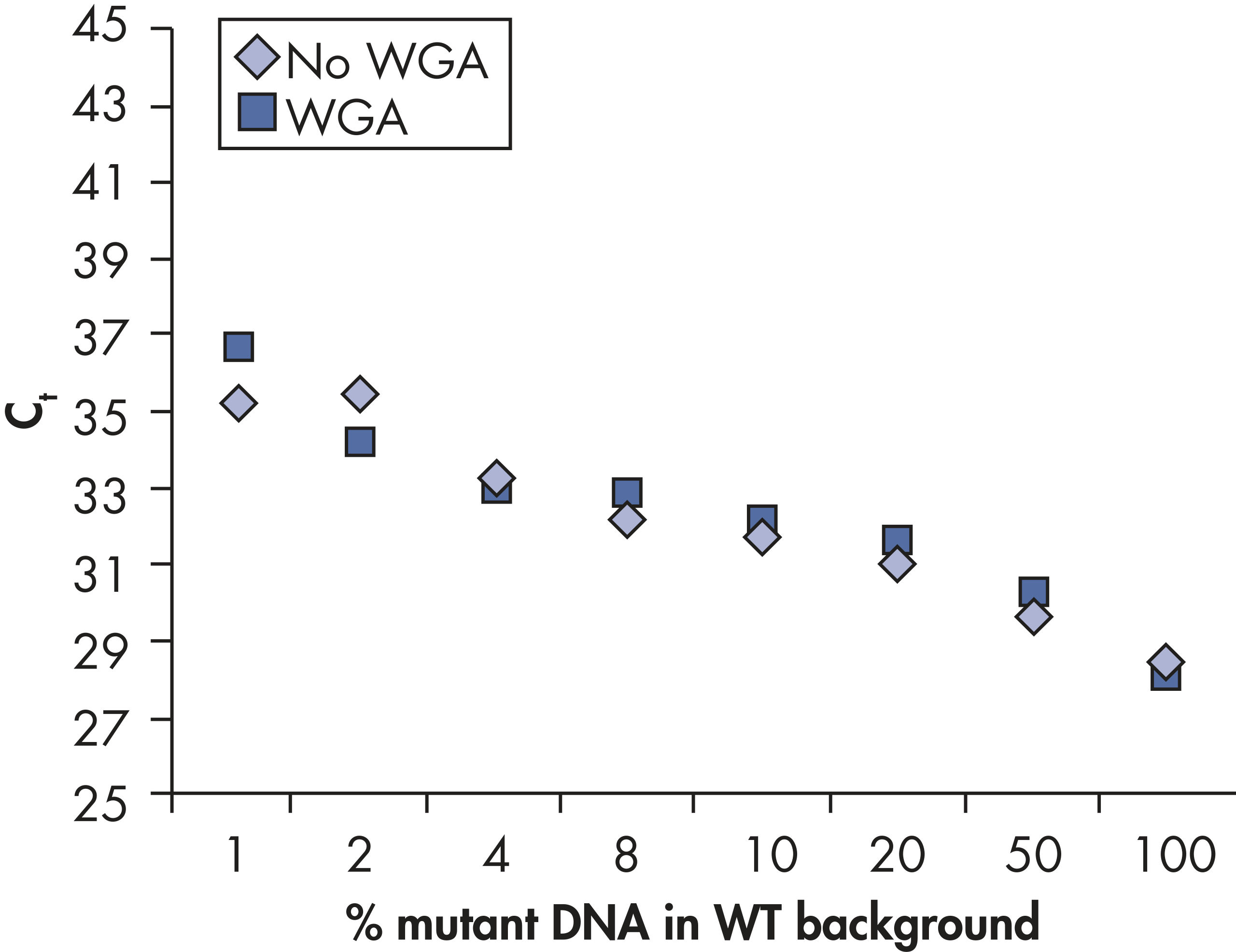
GeneGlobe ID: SMH-3008AA | Cat. No.: 337021 | qBiomarker Somatic Mutation PCR Arrays
qBiomarker™ Somatic Mutation PCR Array Human Tumor Suppressor Genes 384HC
Product Specification
PCR plate and master mix
Target List
APC
The most commonly detected APC inactivation mutations are mainly composed of truncation mutations (due to nonsense mutations and frameshift mutations) and point mutations between codons 1250 and 1578.
ATM
The most commonly detected ATM loss-of-function mutations occur in the FAT, FATC and kinase domains.
CBL
The most frequently occurring mutations in this gene reside in its RING-type, or zinc finger-like, domain in an Asp/Glu-rich (acidic) region likely involved in its ubiquitination activity. Other mutations include p.R420Q and p.K382E, which impair CBL-mediated degradation of cell-surface receptors in a dominant-negative fashion, and p.Y371H, which should reduce tyrosine phosphorylation by the insulin receptor.
CDH1
The most important CDH1 mutations are either missense mutations or frameshift mutations that lead to C-terminal truncation and secreted E-cadherin fragments.
CDKN2A
The most important CDKN2A loss-of-function mutations occur in the consensus ankyrin domain, which lead to the inability to form stable complexes with its targets.
CEBPA
The p.K304_Q305insL mutation lies in the DNA binding basic motif of the protein.
FBXW7
These mutation assays detect FBXW7 variants in either the third or the fourth repeat of the protein's WD40 domain, which is involved in protein-protein interactions.
GNAQ
The mutations queried by these assays all lie in the protein's GTP nucleotide binding domain.
HNF1A
These mutations are expected to interfere with DNA binding.
NF1
The most frequently observed variant of the many NF1 truncation mutations is R304*.
NF2
NF2 is similar to some members of the ERM family of proteins (ezrin, radixin, moesin) and links cell-surface proteins with cytoskeletal components and proteins involved in cytoskeletal dynamics. Mutations in this gene are associated with neurofibromatosis type II which is characterized by nervous system and skin tumors and ocular abnormalities.
NPM1
NPM1 encodes a phosphoprotein that shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm and is thought to be involved in regulation of the ARF/p53 pathway. A number of gene fusion events with NPM1 have been characterized, in particular the anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene on chromosome 2. Mutations in this gene are associated with acute myeloid leukemia.
PTCH1
The detected PTCH1 mutations constitutively activate the Hedgehog signaling pathway and the GLI transcription factors, which increases gene expression involved in tumor cell growth, differentiation, and proliferation.
PTEN
The most commonly detected PTEN loss-of-function mutations either truncate the protein (such as K6fs*4, R130*, R130fs*4, R233*, P248fs*5, and V317fs*3) or cause phosphatase inactivation (such as those at R130 and R173).
RB1
The most recurrent loss-of-function mutations in the RB1 tumor suppressor gene either truncate the protein or disrupt interactions with its binding partners.
SMARCB1
SMARCB1, as part of a complex, relieves repressive chromatin structures, allowing the transcriptional machinery to more effectively access its targets. Mutations in this tumor suppressor gene have been associated with malignant rhabdoid tumors.
STK11
The most commonly detected STK11 inactivation variants either are point mutations or truncate the protein.
TET2
The most common variants of this gene are C-terminal truncations missing its two glutamine-rich regions, all of its metal binding site residues, and a phosphoserine and a phosphotyrosine site.
TP53
The most frequently detected somatic TP53 mutations occur in the DNA-binding domain which disrupt DNA binding and/or protein structure.
TSHR
The represented mutations lie in the transmembrane region of this protein and often induce a gain-of-function by increasing basal cAMP levels but could also make the protein slightly less responsive to TSH stimulation. Other mutations lie in either the cytoplasmic or extracellular domains of the protein.
VHL
Included on the panel are 6 of the most commonly detected VHL point mutations or truncation mutations that lead to loss of tumor suppressor function of the VHL protein.
WT1
The WT1 transcription factor plays an essential role in normal urogenital system development. A small subset of patients with Wilm's tumors contains mutations in this gene.
Product Resources
File Size: 180.58 KBLanguage: English
Resources
Supplementary Protocols (7)
Download Files (1)
Safety Data Sheets (1)
Instrument Technical Documents (2)
Performance Data (3)
Kit Handbooks (1)
White Papers (1)
Articles (1)
Application Notes (1)
Certificates of Analysis (1)
Introducing the qBiomarker™ Somatic Mutation PCR Array Human Tumor Suppressor Genes 384HC, a cutting-edge addition to our qBiomarker Somatic Mutation PCR Arrays lineup, specifically designed for Mutation/Variant Detection applications. This premium product offers unparalleled performance for researchers working with Human models. Leveraging advanced technology, the qBiomarker™ Somatic Mutation PCR Array Human Tumor Suppressor Genes 384HC facilitates accurate and reliable results, making it an indispensable tool for your scientific investigations. Whether you're conducting Mutation/Variant Detection, or any other sophisticated analyses, this product from our qBiomarker Somatic Mutation PCR Arrays collection ensures optimal efficiency and reproducibility for Human studies. Embrace the future of research with qBiomarker™ Somatic Mutation PCR Array Human Tumor Suppressor Genes 384HC and elevate your work to new heights.